
What is Credit Risk, exactly? Credit risk is the risk that a lender takes on when extending credit to a borrower. This is most often caused by the borrower's inability or unwillingness to repay the loan. Credit risk is not only a loss of principal or interest but can also cause cash flow disruptions, and increase collection costs. The risk can be full or partial, and is a primary concern for lenders. A lender should know the types of credit risk that can be considered in determining the appropriate lending strategy.
Measuring
Financial institutions are concerned about the measurement of credit risk. This is due to the fact that analyzing the credit behavior of clients is crucial to avoid future losses. Credit risk management Information Systems (CRMIS), calculate the likelihood that a customer might default on their loan obligations. This information is useful for financial institutions, solidarity groups, and other businesses involved in credit-lending. Here are some tips to measure credit risk:

Analysis
A credit risk analysis uses financial information to estimate the probability that a borrower will default. To predict the possible consequences of default, it uses both company data and external data. This is what makes credit management so important. It helps to minimize the risk and forecast it. Credit risk can be quantified in large measure and has a direct impact upon the activities of financial institutions. These are the fundamentals of credit risk analysis.
Pricing
Recent growth in structured products, credit derivatives and other credit derivatives has led to a lot of interest for sophisticated models to price credit risks. Regulatory concerns and empirical data on default rates have also spurred interest in these models. This article reviews credit risk modeling and examines its development over the last three decades. It also discusses the statistical characteristics of credit spreads over the time period and the quantitative models that are used to determine creditworthiness. The article concludes on some policy implications for credit-risk pricing.
Sector exposure
Financial professionals often mistakenly believe that credit risk and sector exposure are interchangeable. However, although the terms may be different, they are frequently referred to as being the same. The two terms can also be correlated. In fact, a single factor can affect both. Sector exposure, for example, can be a risk factor in a bank's financial health, while credit risk can affect a company's creditworthiness.
Diversification
Diversifying investments across assets and types can reduce credit risk. Diversifying your portfolio will protect you against short-term loss and limit your upside. Diversifying your assets can reduce certain risks such as market volatility due to wars, political conflict and changes in interest rates. By reducing risk and optimizing your returns, diversifying your assets can help you achieve your long term financial goals.
FAQ
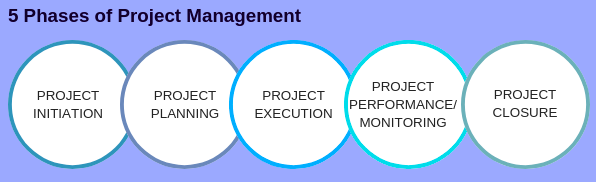
What do we mean when we say "project management"?
Management is the act of managing activities in order to complete a project.
Our services include the definition of the scope, identifying requirements, preparing a budget, organizing project teams, scheduling work, monitoring progress and evaluating the results before closing the project.
What are the key management skills?
Business owners need to have management skills, no matter how small or large they may be. These skills include the ability manage people, finances and resources as well as other factors.
You will need management skills to set goals and objectives, plan strategies, motivate employees, resolve problems, create policies and procedures, and manage change.
As you can see, there's no end to the list of managerial duties!
What kind people use Six Sigma?
Six-sigma will be well-known to anyone who has worked in operations research or statistics. However, anyone involved in any aspect of business can benefit from using it.
Because it requires a high level of commitment, only those with strong leadership skills will make an effort necessary to implement it successfully.
What is the difference between leadership and management?
Leadership is about influencing others. Management is about controlling others.
A leader inspires others while a manager directs them.
A leader motivates people and keeps them on task.
A leader develops people; a manager manages people.
What are the most common errors made by managers?
Sometimes managers make it harder for their employees than is necessary.
They may not be able to delegate enough responsibility to staff or provide adequate support.
Managers often lack the communication skills necessary to motivate and guide their teams.
Some managers create unrealistic expectations for their teams.
Some managers may try to solve every problem themselves instead of delegating responsibility to others.
Statistics
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do you implement a Quality Management Plan (QMP)?
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It helps to improve customer satisfaction and product/service quality by continuously measuring, analyzing, controlling and improving.
QMP stands for Quality Management Process. It is used to guarantee good business performance. QMP is a standard method that improves the production process, service delivery, customer relationship, and overall business performance. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. If the QMP focuses on one aspect, it is called "Process." QMP. If the QMP is focused on a product/service, it's called a QMP. If the QMP focuses on Customer Relationships, it's called a "Product" QMP.
Scope is the most important element in implementing a QMP. Strategy is the second. These elements are as follows:
Scope: This defines what the QMP will cover and its duration. This will be used to define activities that are performed in the first six months of a QMP.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken to achieve the goals set out in the scope.
A typical QMP has five phases: Planning (Design, Development), Implementation (Implementation), and Maintenance. Here are the details for each phase.
Planning: This stage identifies and prioritizes the QMP's objectives. All stakeholders involved in the project are consulted to understand their requirements and expectations. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage involves the creation of the vision, mission, strategies and tactics necessary to implement the QMP successfully. These strategies are executed by creating detailed plans.
Development: Here, the development team works towards building the necessary capabilities and resources to support the implementation of the QMP successfully.
Implementation: This refers to the actual implementation or the use of the strategies planned.
Maintenance: This is an ongoing procedure to keep the QMP in good condition over time.
Additionally, the QMP should include additional items:
Participation by Stakeholders is essential for the QMP's continued success. They are required to actively participate in the planning, design and development of the QMP, as well as the implementation and maintenance phases.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: This is a critical aspect of the QMP. You can use a simplified version if you are only going to be using the QMP for short periods. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation: Another important component of the QMP is cost estimation. Planning is not possible without knowing the amount of money you will spend. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
QMPs should not be considered a static document. It evolves as the company grows and changes. It should be reviewed regularly to ensure that it meets current needs.